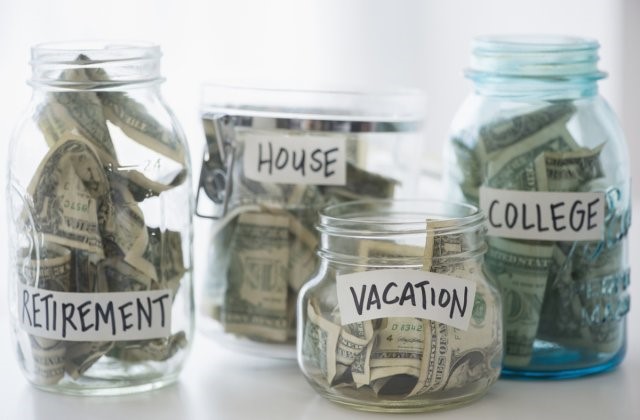
Any finance strategy should be based on clearly defined goals. Two possible courses of action are saving and investment. Each has specific benefits and suitable conditions. Generally, saving helps with short-term goals. In the long-term scenario, investing is preferable. Here is how the strategies compare.
Definitions and OverviewIn the saving scenario, some money is put aside — for instance, weekly. Some individuals use their savings account, others may join a building society. The amount gradually grows until you reach the target value. For example, you could save up for a vacation abroad, a new vehicle or home. The larger the goal — the longer the process.
Some people save up for emergency expenses, with no specific goal in sight. Thereby, they accumulate a fund to fall back on. Whenever their car breaks down, or a boiler needs replacing, there is some guaranteed money available.
Investment is fundamentally different. Here, the money is not merely put aside. You use it to buy things expected to gain value. Typical choices include stocks and property. For instance, if you purchase shares issued by Apple, you are entitled to dividends. When the share price spikes, you may sell off your assets for profit.
Short-term GoalsThe mentioned emergency fund is a must for any family. It allows you to cover force majeure expenses without debt. Few things in life are fully predictable. Hence, be prepared.
Unexpected medical bills, for instance, may cause you to take out a loan. Borrowed money is never free, so you will end up paying more. Importantly, debts should always be the top priority. With every passing day, interest accumulates. The sooner you repay a loan — the less it will cost you.
The optimal size of your rainy day fund is equal to 3 months of expenses. Make sure the account allows instant withdrawal. Sometimes, this may be restricted. Once the target is achieved, you know that financial security is available. However, this is not a reason to stop saving.
Later on, try to contribute at least 10% of your monthly earnings. Once the emergency reserve is filled, you may save up for other goals. Eventually, you should turn to investing to make financial security long-term.
- Chamisa under fire over US$120K donation
- Mavhunga puts DeMbare into Chibuku quarterfinals
- Pension funds bet on Cabora Bassa oilfields
- Councils defy govt fire tender directive
Keep Reading
The best strategies guarantee a source of finance that will exist in a distant future. Short-term goals are important, but saving can hardly provide you with a solid retirement plan. As soon as you turn 30, investment becomes essential.
The primary reason accounting for the choice is inflation. As time goes by, the value of your savings will depreciate. Even if it is not noticeable in the short term, effects accumulated over decades are severe.
The next question is your selection of assets. Stocks are a classic choice due to their long-term value. The stock exchange provides an opportunity to gain sizeable returns over extended periods. Some investors even leave their assets as an inheritance to children and grandchildren.
Value of DiversificationThere are several methods to hedge your investment risks. The key tip is to diversify. The more different assets you include in the portfolio — the better. This way, losses made with one instrument may be covered with profits elsewhere. For instance, if currencies lose value, profits made from stocks can minimize the damage.
Investment is closely related to trading. In essence, a trader also buys assets but sells them off sooner. Explore the opportunities with a demo trading account, which is completely risk-free. Aside from Forex trading, platforms give access to stocks and virtual derivatives (CFDs). The latter allows profiting from price dynamics for commodities, indices, and more.
Both traders and investors may access the market through intermediaries. A broker will register your account and handle all monetary flows. They should also provide professional guidance and learning material.
Save or Invest?Consider the following example. Imagine that your child is going to get married. Would you save or invest to provide money for the wedding? Your answer should depend on the time left. If the kid is still a teenager, investment is preferable as a long-term option. On the other hand, if the wedding is a few years ahead, saving up could suffice.
Another example is a property in the mid-term scenario (5-10 years). Are you sure you will not need the invested money a few years from now? If you choose a deposit instead of investment, withdrawal is easy. Otherwise, you will have to look for cash elsewhere.
The Bottom LineSet clear goals and align your financial strategy with them. Generally, saving through cash deposits is limited to goals five years ahead. Medium-term objectives (five-ten years) may be achieved through saving or investment. Finally, long-term strategies (ten+ years ahead) require a solid and diversified investment portfolio.